Urban Design
Urban Planning
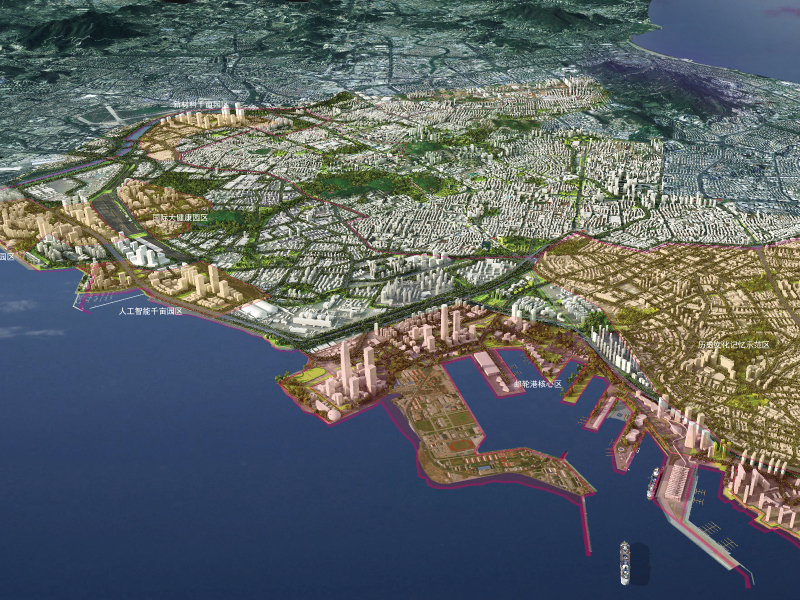
On November 15, 2020, the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) was signed by 15 member states, establishing the world’s largest free trade zone by population and economic potential. Leveraging Qingdao’s strategic coastal location and Shibei District’s cruise port assets, the RCEP Qingdao Pilot Zone was initiated to capitalize on this historic opportunity and revitalize underutilized urban resources. The project anchors Shibei District’s core urban area, serving as a cornerstone of Qingdao’s 14th Five-Year Plan. Spanning 34.2 km² along Jiaozhou Bay’s eastern shore, it integrates five industrial clusters through a "Bay-Riverside New Economic Corridor", driven by three pillars: economic competitiveness, ecological resilience, and enhanced urban services.
Spatial Strategies
1. Polycentric Development – Balanced growth across multiple hubs
2. Connectivity – Integrated transport and blue-green networks
3. Walkability – Pedestrian-first urban fabric
4. Functional Hybridity – Mixed-use districts
5. Cultural Identity – Heritage-informed placemaking
Key Interventions
Industrial Transformation
The redesign converts 18 km of industrial waterfront into a "Golden Coastline" for public life—blending history, culture, commerce, and ecology to reactivate the district.
Government and research teams identify five transformative impacts
1. Elevating Qingdao as a Belt & Road hub and global maritime city
2. Accelerating Northeast Asia’s rise as an international center
3. Strengthening the Yellow River Economic Belt’s port capabilities
4. Leading the Shandong Peninsula Urban Cluster’s economy
5. Forming a "Golden Triangle" with the Shanghai Cooperation Demonstration Zone and Shandong FTZ to reshape Greater Qingdao.
Positioning: "An international free trade innovation district advancing ecological civilization, rooted in Shibei’s natural-cultural legacy and port transformation."
Pillars
Design Tactics
Shibei District, Qingdao City Center
2021-2022
34.2 km²
/图片/idn-02.jpg)
/图片/备选idn-04.jpg)
/图片/备选idn-05.jpg)